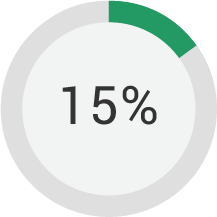
Senegal features a broad and diverse financial landscape, in which people tend to use a combination of different financial institutions, both formal and informal, digital and non-digital. Social networks, including family and friends, are crucial to fulfilling financial needs, allowing borrowing for basic consumption and trusted advice. While overall inclusion is low (15 percent), there are a number of factors in place for greater uptake of financial services, particularly digital financial services. Two thirds of the population live within five kilometers of a mobile money, banking agent or a store or kiosk with over-the-counter services. Most of the population owns a mobile phone, has experiencing with SMS messaging and is aware of mobile money. There are barriers, though, around education, literacy and comfort with financial mechanisms that must be overcome to transition the population from excluded to included.
Photo © World Bank (licensed can be viewed here)
Financial Inclusion
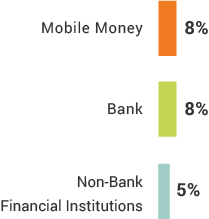
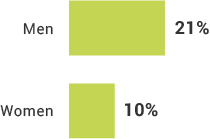
Inclusion By Demographic
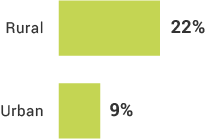
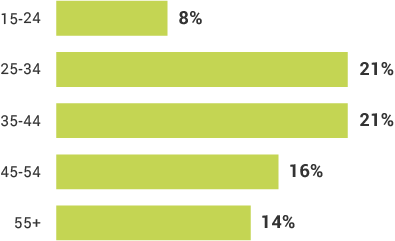
What percent of the population is aware of at least one mobile money provider, but has not used mobile money?
What is the most important financial goal for the typical Senegalese adult?
True or false
Most Senegalese have used a digital financial service
Which mobile money provider has the largest market share?
True or false
Over-the-counter use is more relevant than registered account use of all registered account services (i.e., bank, mobile money and NBFI) combined.
True or false
Of Senegalese adults who save money, saving informally at home is the most frequently used method